
Why Manufacturers Need To Get Stronger at Zero Trust Starting with Microsegmentation
With more unprotected identities and endpoints than any other industry, manufacturing's many attack surfaces are a magnet for cyberattacks. It's not the breach that shuts plants down; it's attackers' lateral movements across networks where they install ransomware and malicious software payloads they'll launch in the future.
The most recent IBM Security X-Force Threat Intelligence Index found that manufacturing is the most attacked industry worldwide, accounting for 23% of all ransomware attacks last year. 61% of breach attempts on manufacturers targeted operational technology (OT) systems essential to manufacturing operations first. A core part of many manufacturers’ OT tech stacks is Industrial Control Systems (ICS). It is often the most vulnerable to an attack because they're designed for process monitoring, reporting, and speed first, with little thought given to security.A typical ICS is among a manufacturer's most porous and unprotected IT assets. Last year Cybersecurity and Infrastructure Security Agency (CISA) warned that advanced persistent threat (APT) criminal gangs are targeting many of the most popular industrial control system (ICS) and SCADA devices. Manufacturers' vulnerabilities are becoming better known through the rapid growth of new endpoint technologies, including IoMT and remote sensing devices deployed to deliver real-time data.
Choose Zero Trust First, And Speed Will Follow
The competitive intensity in manufacturing today prioritizes speed and delivering customer orders on time or early. Resolving to become stronger at zero trust gives manufacturers the one competitive advantage they can't find anywhere else: bulletproof operations and resiliency at a time when their industry is a favorite target.
The manufacturers I've spoken with tell me that closing the gaps between IT and OT systems provides unexpected efficiency and speed gains. Streamlining how employees sign on and use systems that provide least privileged access without requiring lengthy authentication workflows is increasing productivity. Having suppliers and virtual employees as part of a zero trust-based infrastructure saves time and improves collaboration.
“Getting the basics of zero trust right helped us remove the roadblocks of communicating in real-time with suppliers, production partners, and our virtual employees, resulting in efficiency gains measured in hours saved and greater collaboration,” the Chief Operating Officer of a leading technology products manufacturer told me recently. He continued saying “zero trust is table stakes for our distributed operations, it’s core to how we operate and proved to me cybersecurity is a business decision.” He continued by saying that any manufacturing business, including his, would find it tough to recover from a weeks-long disruption due to a ransomware attack.
The efficiency and speed gains manufacturers are looking for are being found in zero trust. Gaining process improvements by closing the IT and OT system gaps is happening, as collaboration and real-time communication with suppliers and production partners keep schedules on track. Best of all, there’s no disruption to production lines because microsegmentation stops any intrusion immediately at the endpoint or threat surface before attackers can breach the network.
What Manufacturers Can Do Now To Get Stronger With Zero Trust
Reducing their threat surfaces with zero trust, starting with microsegmentation, helps increase efficiency, provides speed gains, and averts potentially devastating cyberattacks. Many manufacturers I speak to about zero trust see it as a business decision first, one that controls the risk of their production lines being disrupted.
Here are the most common ways manufacturers are getting started with zero trust. One key takeaway from my conversations with them is that zero-trust security frameworks don’t need to be complex or expensive to be effective. NIST also provides a series of cybersecurity resources for manufacturers.
- Start with microsegmentation to shrink your company’s attack surface. CIOs and security teams say that having the flexibility to define microsegmentation down to the device, identity, and IoMT sensor level is an ideal fit for how they’ve designed their manufacturing IT and OT networks. What makes microsegmentation challenging for manufacturers is how often their endpoints change, including IoMT sensors used throughout the manufacturing process.
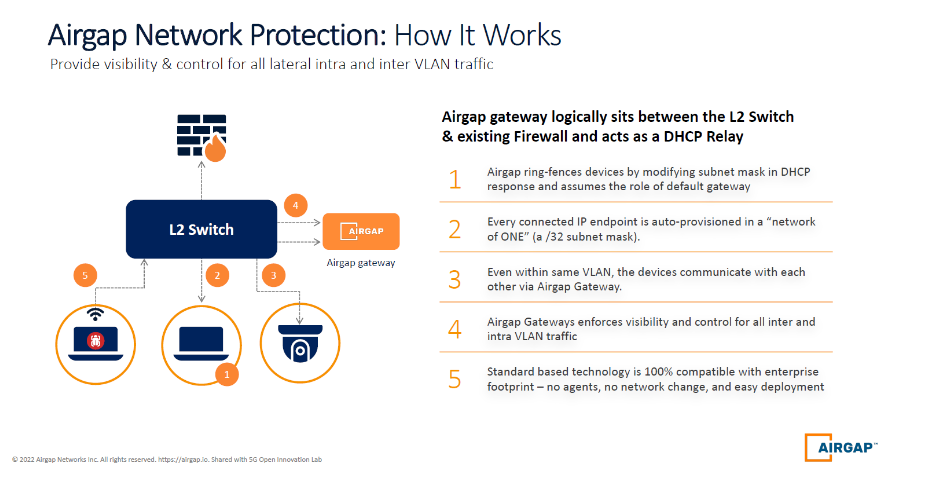
- My team and I designed AirGap’s Zero Trust Everywhere solution to adapt quickly across manufacturers' constantly changing endpoints, which are the most fluid attack surfaces they’re protecting today. We invented an agentless segmentation technology that would alleviate the need to install and keep endpoint agents patched and updated. That’s a significant cost and time saver for our manufacturing customers because we handle that with the AirGap Gateway. The following graphic explains how AirGap network protection is designed to reduce threat surfaces and eliminate an attacker's potential for lateral movement.
- Make it a high priority to protect identities with MFA, SSO, or passwordless authentication. Core to zero trust is authenticating every device, session, and resource request for each identity on a network, and that starts by treating every human and machine identity as the security perimeter of your network.
- 74% of breaches start with privileged access abuse and quickly escalate into attacks on Active Directory (AD) and other core systems that control privileged access credentials. CIOs consider MFA a quick win as part of their zero trust strategy because it’s a part of the framework that lends itself well to measuring progress. ''We know nearly all account compromise attacks can be stopped outright, just by using MFA. It's a proven, effective way to thwart bad actors,'' said Karen S. Evans, managing director of Cyber Readiness Institute.
- Take on the challenge of securing endpoints, starting with those in the IT and OT systems gap. ICS-based endpoints are the most challenging to protect but also the most at risk of an intrusion attempt. Many sensors and monitoring systems are part of a typical ICS, making protecting an OT tech stack more challenging. AirGap’s proven ability to secure endpoints at the IP endpoint alleviates the need to connect to every sensor, reducing the blast radius if any intrusion attempts to the sensor. Manufacturing runs on endpoints as conduits to e-commerce, supplier, and customer transactions. Getting security right on endpoints is core to a successful zero-trust strategy.
The Future of Manufacturing Security Is Zero Trust
The bottom line is that zero trust is the efficiency and speed multiplier manufacturers are looking for and need to compete in the year ahead.
With manufacturing considered a soft target by attackers and the world industry leader in ransomware attacks, every manufacturer needs to get started on their zero trust security framework and strategy. This article aims to provide the three most common and successful areas to start. Manufacturing’s future will be defined by how successfully it adopts zero trust and secures the proliferating number of endpoints created to serve customers and grow their businesses.
